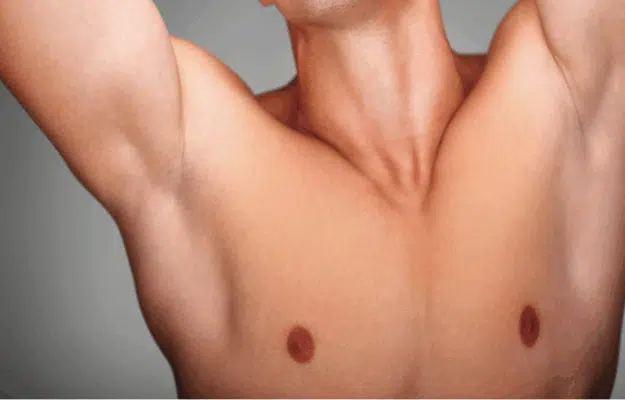
Gynecomastia is a condition that causes the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It can develop at any stage of life, often due to hormonal changes, weight fluctuations, medication side effects, or underlying health conditions. While some cases resolve on their own, others persist and may require surgical intervention.
One of the most common questions regarding gynecomastia surgery is about the appropriate age for undergoing the procedure. Although the condition can appear in childhood or adolescence, surgery is not always recommended for younger patients. A minimum age requirement ensures that suitable candidates are chosen for treatment, allowing for the best possible outcomes.
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a condition that leads to the enlargement of breast tissue in men. It is relatively common and can be triggered by a range of factors, including hormonal imbalances, the use of certain medications, obesity, or genetic predisposition. While not usually harmful in a medical sense, gynecomastia can cause significant physical and psychological discomfort, often leading individuals to seek treatment to restore a more masculine chest appearance.
What Causes Gynecomastia?
At its core, gynecomastia is the result of an imbalance between two key hormones—testosterone and oestrogen. Testosterone is primarily responsible for male characteristics such as muscle mass and body hair, while oestrogen, although present in smaller amounts in men, plays a role in regulating fat distribution and breast tissue development.
RELATED: What Causes Gynecomastia?
During puberty, hormonal fluctuations are common, and many teenage boys experience temporary breast enlargement. In most cases, as hormone levels stabilise with age, the condition resolves on its own. However, for some, the excess breast tissue does not disappear, leading to persistent gynecomastia into adulthood.
RELATED: Does Gynecomastia Go Away?
Beyond puberty, other factors can contribute to the development of gynecomastia. Obesity is a well-known cause, as excess fat can lead to higher oestrogen production, promoting breast tissue growth. Certain medications, including anabolic steroids, antidepressants, and drugs used to treat heart conditions, can also disrupt hormonal balance. Additionally, medical conditions such as liver disease, thyroid disorders, and kidney problems may contribute to gynecomastia by altering hormone levels.
Who Can Be Affected by Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia can occur at any stage of life, from infancy to old age. In newborns, the condition is often due to the transfer of maternal oestrogen and typically resolves within a few weeks. During adolescence, it is relatively common, affecting a significant percentage of teenage boys, with most cases resolving naturally within a couple of years. However, when gynecomastia persists beyond puberty or develops later in life, it often requires medical evaluation and, in some cases, surgical treatment.
For adult men, the condition can develop due to age-related hormonal changes, weight gain, or the use of medications that affect hormone levels. It is particularly common in middle-aged and older men, as testosterone levels naturally decline with age. In such cases, the condition is less likely to resolve on its own, leading many individuals to explore treatment options, including gynecomastia surgery.
Is Gynecomastia Surgery the Right Solution?
For men who experience long-term or severe gynecomastia, surgery can be an effective treatment to restore a flatter, more masculine chest contour. The procedure typically involves the removal of excess glandular tissue, fat, or a combination of both. Many men who undergo gynecomastia surgery report a significant improvement in their self-confidence and overall quality of life.
RELATED: How To Get Rid Of Gynecomastia
While some cases of gynecomastia may improve with lifestyle changes, weight loss, or adjustments to medication, others persist regardless of these efforts. If the condition is causing emotional distress or physical discomfort, consulting with a specialist can help determine the most appropriate course of action.
At Centre for Surgery, we understand the impact that gynecomastia can have on confidence and daily life. Our experienced plastic surgeons provide personalised consultations to assess each case individually, offering expert advice on whether surgery is the best option. If you are struggling with persistent gynecomastia and seeking a long-term solution, a consultation with our team can help you take the first step towards a more confident you.
RELATED: Gynecomastia Surgery FAQs – Q&A about Male Breast Reduction
Is Surgery a Suitable Option for Adolescent Gynecomastia?
During adolescence, hormonal fluctuations are a natural part of development, and these changes can sometimes lead to the temporary enlargement of breast tissue in males. This condition, known as gynecomastia, is quite common in teenage boys and is usually caused by an imbalance between testosterone and oestrogen.
For most adolescents, this breast tissue enlargement is temporary and tends to resolve on its own as hormone levels stabilise, usually by the age of 18. Because of this, surgeons generally recommend waiting before considering surgical treatment. Performing gynecomastia surgery too early can be counterproductive, as there is a possibility that the condition will resolve naturally or that new tissue growth may occur if hormone fluctuations are still ongoing.
Why Do Surgeons Advise Waiting Until Adulthood?
One of the key reasons for delaying surgery until adulthood is that adolescent gynecomastia often improves without medical intervention. In many cases, once puberty is complete and testosterone levels rise, the excess breast tissue shrinks or disappears entirely. If surgery is performed too early, before hormone levels have stabilised, there is a risk that the breast tissue may return, requiring further treatment in the future.
However, in cases where gynecomastia is particularly severe or is causing significant emotional distress, exceptions can sometimes be made. If the condition is affecting a young person’s confidence, mental well-being, or ability to participate in activities such as sports or social events, a specialist may assess whether early intervention is appropriate.
Alternative Treatment Options for Adolescents
For teenagers experiencing mild to moderate gynecomastia, there are alternative approaches to managing the condition before considering surgery. In some cases, lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and increasing physical activity, can help to reduce fat deposits in the chest area, improving overall appearance. Although glandular tissue itself will not shrink with exercise, reducing excess fat can make the condition less noticeable.
RELATED: Can You Get Rid of Gynecomastia with Exercise?
Certain medications can also be prescribed in specific cases, particularly if the gynecomastia is linked to hormonal imbalances. These treatments work by blocking the effects of oestrogen or stimulating testosterone production. However, medication is not suitable for all cases and is generally only considered when the condition is persistent and causing distress.
Persistent Gynecomastia in Adulthood: When Surgery Becomes a Viable Option
For many men, gynecomastia that develops during adolescence naturally resolves as hormone levels stabilise. However, when the condition persists into adulthood—particularly in the early 20s and beyond—it is much less likely to improve without medical intervention. At this stage, surgery often becomes the most effective treatment option for removing excess breast tissue and restoring a more masculine chest contour.
Why Does Gynecomastia Persist Into Adulthood?
By the time a man reaches his 20s, hormone levels have generally stabilised. If gynecomastia remains, it is unlikely that the condition will resolve on its own. The persistence of enlarged breast tissue at this stage suggests that the initial cause—whether hormonal fluctuations, genetics, or other factors—has resulted in permanent glandular tissue growth that will not shrink over time.
When consulting with a plastic surgeon about gynecomastia surgery, candidates are often advised to undergo medical tests to determine whether any specific underlying causes need to be addressed. Certain health conditions, such as thyroid disorders, liver disease, or hormonal imbalances, can contribute to the persistence of gynecomastia. Additionally, the use of medications such as anabolic steroids, antidepressants, or drugs that affect hormone levels may play a role.
If a clear underlying cause is identified, managing or treating this issue is usually recommended before proceeding with surgery. In some cases, addressing the root cause—such as discontinuing a specific medication—can help reduce the severity of gynecomastia. However, if the glandular tissue has already become well-established, surgical removal remains the only definitive solution.
Gynecomastia Surgery Later in Life
While many men seek gynecomastia surgery in their 20s, others may choose to undergo the procedure much later in life. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, leading to changes in body composition, including an increase in fat deposits and potential breast tissue growth. Weight gain, hormonal fluctuations, and the use of certain medications can also contribute to the development of gynecomastia in middle-aged and older men.
RELATED: Gynecomastia vs Chest Fat – How to Tell the Difference
For some, gynecomastia may be a new development in later life, while for others, it may be a condition they have struggled with since adolescence but have only recently decided to seek treatment for. Regardless of when the condition occurs, gynecomastia surgery remains an effective option for those seeking a long-term solution.