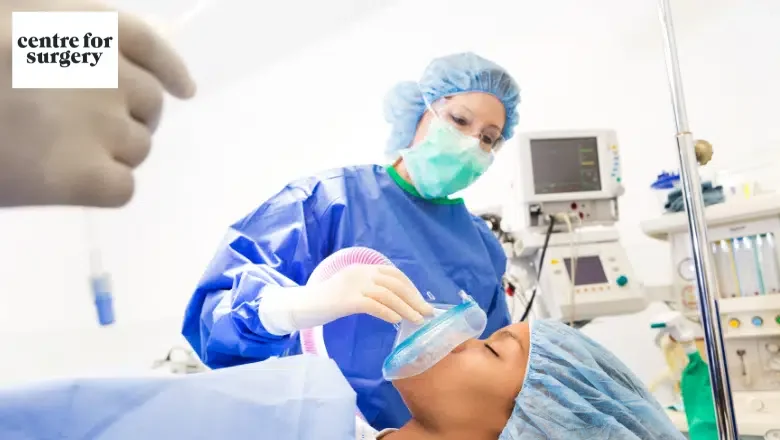
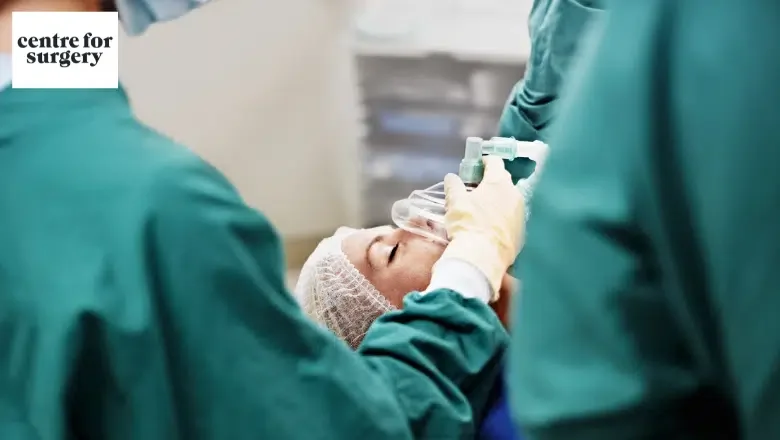
What is Twilight Sedation?
Twilight sedation, also known as conscious sedation or moderate sedation, is a type of medical procedure that uses medication to help patients relax and feel less anxious during a procedure or surgery. The goal of twilight sedation is to maintain a state of consciousness in the patient so that they are able to follow instructions and respond to questions or stimuli, while still experiencing a level of sedation and relaxation.
RELATED: Dangers of Using Twilight Sedation for Cosmetic Surgery Procedures
The medication used in twilight sedation is delivered intravenously (IV). The specific medication will depend on the type of procedure, the patient’s medical history, and the anaesthetist’s preference.
Common side effects of twilight sedation can include drowsiness, confusion, nausea, and temporary memory loss. However, these side effects are typically mild and short-lived.
RELATED: Anaesthesia for Cosmetic Surgery
Benefits of twilight sedation
How does twilight sedation differ from general anaesthesia?
When it comes to anaesthesia for medical procedures and surgeries, twilight sedation and general anaesthesia are two commonly used methods, each with its distinct characteristics and applications.
Depth of Sedation: A fundamental difference lies in the level of sedation each method offers. Twilight sedation induces a milder form of sedation, allowing patients to remain semi-conscious and responsive. In contrast, general anaesthesia involves a deeper sedation level, typically rendering the patient completely unconscious. This difference in sedation depth directly impacts the patient’s awareness and responsiveness during the procedure.
Medications Employed: The types of medications used to achieve these sedation levels also vary. Twilight sedation usually involves intravenous (IV) medications that relax the patient and reduce pain. On the other hand, general anaesthesia often combines IV with inhaled medications, achieving a state of unconsciousness where the patient feels no pain and has no memory of the procedure.
Monitoring Needs: The monitoring of patients under twilight sedation and general anaesthesia also differs. For twilight sedation, standard monitoring techniques like pulse oximetry and blood pressure measurements are typically sufficient. Conversely, general anaesthesia requires more comprehensive monitoring, including electrocardiogram (ECG) and end-tidal carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, to ensure the patient’s safety throughout the procedure.
Recovery Time: Another key difference is the recovery period post-procedure. Patients recovering from twilight sedation usually experience a quicker return to normalcy, often resuming regular activities within hours.
Procedure Suitability: The choice between twilight sedation and general anaesthesia often depends on the nature of the procedure itself. Twilight sedation is suitable for a broad range of minor procedures and diagnostic tests, offering sufficient comfort and relaxation without deep sedation. General anaesthesia is preferred for more invasive surgeries or procedures that demand complete immobility and absence of consciousness for extended periods.
RELATED: Types of Anaesthesia Used in Plastic Surgery
Potential side effects of twilight sedation
While twilight sedation is widely regarded as a safe and effective method for easing the experience of medical procedures, it’s important for patients to be mindful of possible side effects. These can vary in intensity and duration but are generally manageable and temporary.
Confusion and disorientation may occur, often lasting just a short while post-procedure. Patients might also feel notably drowsy for several hours afterwards, making it crucial to steer clear of driving or handling heavy machinery during this period. Nausea and vomiting are other potential side effects, which can stem from both the sedation and the procedure itself.
A less common, yet noteworthy, side effect is temporary memory loss. Patients might find it hard to recall specifics of the procedure or events that happen shortly after. Although rare, there’s a possibility of allergic reactions to the sedative, indicated by symptoms such as itching, hives, difficulty breathing, and an accelerated heartbeat. Even more rarely, the sedation can lead to respiratory depression, marked by reduced or slow breathing.
Which cosmetic procedures can be performed using twilight sedation?
Twilight sedation can be used for a variety of cosmetic procedures to help patients feel more relaxed and comfortable during the procedure. Some of the most common cosmetic procedures that are performed using twilight sedation include:
- Dermal fillers: Twilight sedation can be used to help patients feel more relaxed and comfortable during the injection of dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid.
- Laser skin resurfacing: Twilight sedation can be used to help patients feel more relaxed and comfortable during laser skin resurfacing procedures, which can help to reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and sun damage.
- Body contouring: Twilight sedation can be used to help patients feel more relaxed and comfortable during body contouring procedures, such as micro liposuction.
- Plastic surgery: Twilight sedation can also be used to help patients feel more relaxed and comfortable during plastic surgery procedures, such as blepharoplasty, mini facelift or one-stitch facelift
Is Twilight Sedation the Right Choice for You? Key Considerations
Choosing twilight sedation for your medical procedure involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure it’s the best fit for your needs. First and foremost, your overall health plays a crucial role in this decision. Conditions such as heart disease or respiratory problems might make twilight sedation less suitable for you. A detailed conversation with your healthcare provider about your medical history is essential in determining if this form of sedation aligns with your health needs.
Medications you’re currently taking also come into play. For instance, if you’re on opioids or benzodiazepines, there’s a heightened risk of complications due to possible interactions with the sedation drugs. Your healthcare provider will review your medication list to ensure twilight sedation is a safe option for you.
The type of procedure you’re undergoing is another important factor. Not all surgeries are ideal candidates for twilight sedation; certain complex operations might necessitate general anaesthesia or may be better suited to local anaesthesia, depending on your doctor’s assessment and your personal comfort and safety preferences.
Lastly, personal preference matters significantly. Some patients might opt for the deeper sedation that general anaesthesia offers or prefer the minimal intervention of local anaesthesia. At Centre for Surgery, the preference leans towards general anaesthesia for ensuring maximum comfort and safety during surgeries.